A) will import oranges.
B) will export oranges.
C) will either export oranges or export oranges,but it is not clear from the given information.
D) would have nothing to gain either from exporting or importing oranges.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The principle of comparative advantage asserts that
A) not all countries can benefit from trade with other countries.
B) the world price of a good will prevail in all countries,regardless of whether those countries allow international trade in that good.
C) countries can become better off by exporting goods,but they cannot become better off by importing goods.
D) countries can become better off by specializing in what they do best.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Import quotas and tariffs make domestic sellers better off and domestic buyers worse off.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The world price of cotton is the highest price of cotton observed anywhere in the world.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-19.On the diagram below,Q represents the quantity of textiles and P represents the price of textiles.
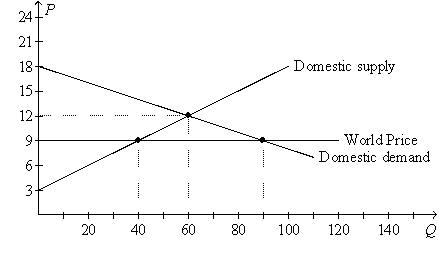 -Refer to Figure 9-19.With free trade,the country for which the figure is drawn will
-Refer to Figure 9-19.With free trade,the country for which the figure is drawn will
A) export 30 units of textiles.
B) export 50 units of textiles.
C) import 30 units of textiles.
D) import 50 units of textiles.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists view the fact that Florida grows oranges,Texas pumps oil,and California makes wine as
A) confirmation of the virtues of free trade.
B) confirmation of the infant-industry argument.
C) confirmation that free trade agreements are not necessary.
D) confirmation that specialization in absolute advantage works.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If Honduras were to subsidize the production of wool blankets and sell them in Sweden at artificially low prices,the Swedish economy would be worse off.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In analyzing the gains and losses from international trade,to say that Moldova is a small country is to say that
A) Moldova can only import goods; it cannot export goods.
B) Moldova's choice of which goods to export and which goods to import is not based on the principle of comparative advantage.
C) only the domestic price of a good is relevant for Moldova; the world price of a good is irrelevant.
D) Moldova is a price taker.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Free trade allows firms to realize economies of scale,resulting in higher costs of production.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a tariff is placed on watches,the price of both domestic and imported watches will rise by the amount of the tariff.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a country abandons a no-trade policy in favor of a free-trade policy.If,as a result,the domestic price of pistachios decreases to equal the world price of pistachios,then
A) that country becomes an exporter of pistachios.
B) that country has a comparative advantage in producing pistachios.
C) at the world price,the quantity of pistachios demanded in that country exceeds the quantity of pistachios supplied in that country.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Domestic producers of a good become better off,and domestic consumers of a good become worse off,when a country begins allowing international trade in that good and
A) the country becomes an importer of the good as a result.
B) the world price exceeds the domestic price of the good that prevailed before international trade was allowed.
C) other countries have a comparative advantage,relative to the country in question,in producing the good.
D) total surplus does not change as a result.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A quota is
A) a tax placed on imports.
B) a limit on the quantity of imports.
C) a tax on exports to other countries.
D) an excess of exports over imports.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-16.The figure below illustrates a tariff.On the graph,Q represents quantity and P represents price. 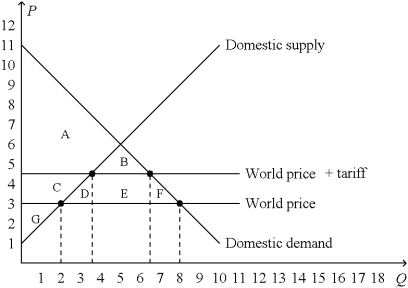 -Refer to Figure 9-16.The tariff
-Refer to Figure 9-16.The tariff
A) decreases producer surplus by the area C,decreases consumer surplus by the area C + D + E,and decreases total surplus by the area D + F.
B) increases producer surplus by the area C,decreases consumer surplus by the area C + D + E + F,and decreases total surplus by the area D + F.
C) creates government revenue represented by the area B + E and decreases total surplus by the area D + E + F.
D) increases producer surplus by the area C + G and creates government revenue represented by the area D + E + F.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a country's domestic price of a good is lower than the world price,then that country has a comparative advantage in producing that good.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9-15 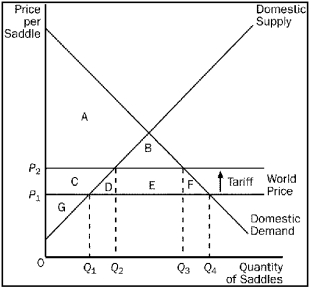 -Refer to Figure 9-15.For the saddle market,area E represents
-Refer to Figure 9-15.For the saddle market,area E represents
A) government's revenue from the tariff.
B) producer surplus after the tariff becomes effective.
C) the decrease in consumer surplus,relative to the free-trade situation,as a result of the tariff.
D) the decrease in total surplus,relative to the free-trade situation,as a result of the tariff.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Domestic producers of a good become worse off,and domestic consumers of a good become better off,when a country begins allowing international trade in that good and
A) the country becomes an importer of the good as a result.
B) the world price exceeds the domestic price of the good that prevailed before international trade was allowed.
C) the country in question has a comparative advantage,relative to other countries,in producing the good.
D) total surplus does not change as a result.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some goods can be produced at low cost only if they are produced in large quantities.This phenomenon is called
A) marginal cost of production.
B) marginal benefit of size.
C) economies of scale.
D) economies of production.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The history of the textile industry raises important questions for economic policy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A country has a comparative advantage in a product if the world price is
A) lower than that country's domestic price without trade.
B) higher than that country's domestic price without trade.
C) equal to that country's domestic price without trade.
D) not subject to manipulation by organizations that govern international trade.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 68
Related Exams