A) 90 million
B) 150 million
C) 160 million
D) 230 million
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a minimum-wage law forces the wage to remain above the level that balances supply and demand,there are more workers willing to work than there are jobs,so some workers are unemployed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The unemployed who quit their jobs,were fired for cause,or just entered the labor force are eligible for unemployment insurance.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Between the 1940s and today,union membership in the U.S.
A) rose from about one-eighth to one-third of the labor force.
B) rose from about one-third to one-half of the labor force.
C) fell from about one-half to one-third of the labor force.
D) fell from about one-third to one-eighth of the labor force.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Minimum-wage laws and unions are similar to each other but different from efficiency wages in that minimum-wage law and unions
A) cause unemployment,but efficiency wages do not.
B) cause the quantity of labor supplied to exceed the quantity of labor demanded,but efficiency wages do not.
C) cause wages to be above the equilibrium level.
D) prevent firms from lowering wages in the presence of a surplus of workers.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Structural unemployment is often thought to explain relatively short spells of unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People who are unemployed because of job search are best classified as
A) cyclically unemployed.
B) structurally unemployed.
C) frictionally unemployed.
D) discouraged workers.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a cause of frictional unemployment?
A) the destruction of manufacturing jobs
B) a worker leaving a job to find one with better benefits
C) minimum-wage laws
D) unemployment insurance
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If all workers and all jobs were the same such that all workers were equally well suited for all jobs,then there would be no
A) cyclical unemployment.
B) frictional unemployment.
C) natural rate of unemployment.
D) structural unemployment.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Frictional unemployment is thought to explain
A) relatively short spells of unemployment,as is structural unemployment.
B) relatively long spells of unemployment,as is structural unemployment.
C) relatively short spells of unemployment,while structural unemployment is thought to explain relatively long spells of unemployment.
D) relatively long spells of unemployment,while structural unemployment is thought to explain relatively short spells of unemployment.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Minimum-wage laws matter most for the least skilled and least experienced members of the labor force,such as teenagers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Maxine,the owner of a furniture company,decides to raise the wages of her workers even though she faces an excess supply of labor.Her decision
A) might increase profits if it attracts a better pool of workers to apply for her firm's jobs.
B) will increase the excess supply of labor.
C) may increase the quality of her work force.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a union and a firm cannot reach an agreement on the terms of employment,then the union can organize a withdrawal of labor from the firm,called a strike.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Minimum-wage laws can keep wages
A) above equilibrium and cause a surplus of labor.
B) above equilibrium and cause a shortage of labor.
C) below equilibrium and cause a surplus of labor.
D) below equilibrium and cause a shortage of labor.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginally attached workers are people who
A) are looking for a better job than they currently have.
B) are not working and are not looking for work,but would work if asked.
C) are working part-time while they go to school or get training for a better job.
D) are only a few years from retirement.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) Unions raise the wages above the level that would prevail in competitive markets.
B) Unions reduce the quantity of labor demanded,cause some workers to be unemployed,and reduce the wages in the rest of the economy.
C) Critics argue that the allocation of labor resulting from unions is both inefficient and inequitable.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 28-1
Labor Data for Wrexington
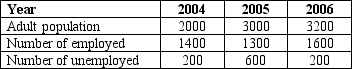 -Refer to Table 28-1.The number of adults not in the labor force of Wrexington in 2004 was
-Refer to Table 28-1.The number of adults not in the labor force of Wrexington in 2004 was
A) 200
B) 400
C) 600
D) 1800
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Bureau of Labor Statistics defines discouraged workers as marginally attached workers who have given a job-market related reason for not currently looking for a job.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who of the following would be included in the Bureau of Labor Statistics' "unemployed" category?
A) Cemal,a full-time student who is not looking for work
B) Halim,who is on temporary layoff
C) Zeynep,who has retired and is not looking for work
D) All of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From time to time,the demand for workers has risen in one region of the United States and fallen in another.This illustrates
A) frictional unemployment created by efficiency wages.
B) structural unemployment created by efficiency wages.
C) frictional unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
D) structural unemployment created by sectoral shifts.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 501 - 520 of 533
Related Exams