B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of signaling?
A) Pat is considering the purchase of a used car. Before making the purchase he has the car checked by an auto mechanic.
B) Zach is applying for a new life insurance policy. Before writing the policy, the insurance company requires Zach to be examined by a doctor.
C) Denise is applying for a new job. Before hiring her, the firm requires Denise to take a drug test.
D) Marcus is planning to ask for Chaquila's hand in marriage. Before asking her, he buys her a box of her favorite chocolates and takes her to dinner at her favorite restaurant.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 22-2
A wireless telephone service provider offers three service plans to its consumers.  -Refer to Scenario 22-2. By offering consumers these choices, the wireless telephone provider is
-Refer to Scenario 22-2. By offering consumers these choices, the wireless telephone provider is
A) signaling to customers that they offer great customer service.
B) screening customers to reveal how much they plan to use the service.
C) creating asymmetric information because only the firm knows the true cost of the service.
D) engaging in a principal-agent problem
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The state of Massachusetts requires all citizens to purchase medical insurance or face a monetary penalty when filing their taxes. The penalty is significantly less than the average annual insurance premium. Moreover, the state requires insurance companies to issue policies to anyone who applies, regardless of their health at the time of application. Which of the following examples describes the inherent adverse selection problem?
A) Tricia purchases an insurance policy through her employer and visits her doctor for annual check-ups.
B) Sue purchases insurance only after learning that she has cancer.
C) Mike pays the penalty rather than purchasing insurance because it is cheaper for him than paying insurance premiums and he is generally in good health.
D) Both b and c are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the field of study called political economy, economists make use of insights from the field of psychology.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If preferences exhibit the property of transitivity, then
A) the preferences are irrational.
B) individuals prefer more government involvement in private markets than do people whose preferences are not transitive.
C) preferences change over time more quickly than when preferences are not transitive.
D) preferences satisfy one of the properties assumed to be desirable by Kenneth Arrow in Social Choice and Individual Values.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adverse selection is
A) the tendency of a person who is imperfectly monitored to engage in dishonest or otherwise undesirable behavior.
B) an action taken by an uninformed party to induce an informed party to reveal information.
C) the failure of majority voting to produce transitive preferences for society.
D) the tendency for the mix of unobserved attributes to become undesirable from the standpoint of an uninformed party.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Normally, we expect voters' preferences to exhibit a property called
A) transitivity.
B) transversality.
C) normality.
D) universality.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 22-3 At issue in a particular city vote is how much to spend, per person, on road repair next year. Among the 10,000 voters, 2,900 prefer to spend $500 per person, but no more; 2,200 prefer to spend $600 per person, but no more; 1,900 prefer to spend $800 per person, but no more; 1,600 prefer to spend $1,200 but no more, and 1,400 prefer to spend $1,400 per person, but no more. -Refer to Scenario 22-3. If there is a vote on whether to spend $600 per person or $800 per person, the median voter will vote to spend
A) $800 per person and the voting outcome will be $800 per person.
B) $800 per person and the voting outcome will be $600 per person.
C) $600 per person and the voting outcome will be $800 per person.
D) $600 per person and the voting outcome will be $600 per person.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ihaveathousandfriends Social Networking firm had a remarkably profitable year. As a result, its employees expect to receive bonus checks. Which of the following insights into human behavior do the employees exhibit?
A) People are overconfident.
B) People care about fairness.
C) People are reluctant to change their minds.
D) People are inconsistent over time.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of moral hazard?
A) a driver is arrested for drunk driving
B) a pet-sitter being paid to walk a dog for one hour per day only walks the dog for 20 minutes per day
C) a thief steals a car
D) All of the above are examples of moral hazard.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Condorcet paradox
A) demonstrates that the order in which one votes on options may influence the outcome.
B) demonstrates that majority voting by itself may not reveal the outcome that society wants.
C) disproves Arrow's impossibility theorem.
D) Both a and b are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Frequently it is the case that: (1) A worker knows more than his employer about how much effort he puts into his job, and (2) the seller of a used car knows more than the buyer about the car's condition.
A) Neither (1) nor (2) serves as an example of asymmetric information.
B) Both (1) and (2) serve as examples of asymmetric information.
C) Neither (1) nor (2) serves as an example of a hidden action.
D) Both (1) and (2) serve as examples of hidden action.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-7
Suppose that residents of a town are asked to vote on the best way to improve the safety of an intersection. The three choices are: a stoplight, a 4-way stop, and a 2-way stop. The voters are divided into three groups based on their preferences.
Voter Type 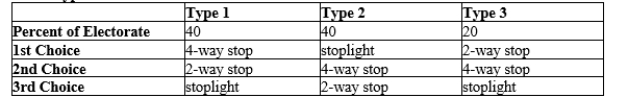 -Refer to Table 22-7. If the first vote pits a 2-way stop against a 4-way stop and the second vote pits a stoplight against the winner of the first vote, then the outcome is as follows:
-Refer to Table 22-7. If the first vote pits a 2-way stop against a 4-way stop and the second vote pits a stoplight against the winner of the first vote, then the outcome is as follows:
A) 2-way stop wins the first vote and 2-way stop wins the second vote, so the town installs a 2-way stop.
B) 2-way stop wins the first vote and stoplight wins the second vote, so the town installs a stoplight.
C) 4-way stop wins the first vote and 4-way stop wins the second vote, so the town installs a 4-way stop.
D) 4-way stop wins the first vote and stoplight wins the second vote, so the town installs a stoplight.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The problem that arises when one person performs a task on behalf of another person is called
A) the hidden characteristics problem.
B) the lemons problem.
C) moral hazard.
D) adverse selection.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-7
Suppose that residents of a town are asked to vote on the best way to improve the safety of an intersection. The three choices are: a stoplight, a 4-way stop, and a 2-way stop. The voters are divided into three groups based on their preferences.
Voter Type  -Refer to Table 22-7. Based on the information in the table, which of the following statements is true?
-Refer to Table 22-7. Based on the information in the table, which of the following statements is true?
A) In a vote between a 2-way stop and a stoplight, stoplight wins because 40% of voters have stoplight as their 1st choice.
B) In a vote between a 2-way stop and a 4-way stop, the 4-way stop wins getting 80% of the total vote.
C) In a vote between a 4-way stop and a stoplight, there is a tie because each gets 40% of the vote.
D) None of the above are true.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In economics, a difference in access to relevant knowledge is called a(n)
A) relevancy frontier.
B) knowledge gap.
C) information asymmetry.
D) information equilibrium.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-15
Diane, Henry, and Linda are voting for who to promote. They can only promote one candidate. Their preferences are given in the table below. 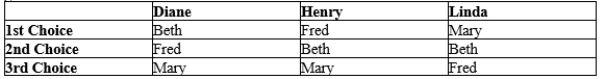 -Refer to Table 22-15. If elections were held where voters choose either Fred or Beth, and then choose either the winner or Mary, what would the results be?
-Refer to Table 22-15. If elections were held where voters choose either Fred or Beth, and then choose either the winner or Mary, what would the results be?
A) Fred would win the first and second election.
B) Fred would win the first election and Mary would win the second.
C) Beth would wind the first and second election.
D) Beth would win the first election and Mary would win the second.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Riley travels a great deal, and over the past several years he has read dozens of reviews of hotel chains, all of which rave about the clean rooms and great service at Comeon Inns. Last month, Riley checked into a room at a Comeon Inn for the first time, only to find the room filthy and the service lousy. He decided the Comeon Inn chain is inferior to other hotel chains.
A) Riley was irrational to have believed the reviews that he had read.
B) Riley was rational to have changed his mind about Comeon Inns based on his one experience.
C) Riley is an example of someone who gives too much weight to a small number of vivid observations.
D) Riley is an example of someone who is reluctant to change his mind.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Brandon is considering buying a used car but he first downloads a report from the internet that shows the history of accidents and major repairs conducted on the car. This action is called
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 461
Related Exams