Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model, sticky wages, sticky prices, and misperceptions about relative prices
A) have temporary effects.
B) explain why the short run aggregate supply curve might shift.
C) explain why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
D) explain monetary neutrality.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Microeconomic substitution is impossible for the economy as a whole because
A) money is a veil.
B) real GDP measures the total quantity of goods and services produced by all firms in all markets.
C) the prices of some goods and services adjust sluggishly in response to changing economic conditions.
D) a lower price level increases real wealth, which stimulates spending by consumers and vice-versa.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price level falls, the real value of a dollar
A) rises, so people will want to buy more. This response helps explain the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
B) rises, so people will want to buy more. This response shifts aggregate demand to the right.
C) falls, so people will want to buy less. This response helps explain the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
D) falls, so people will want to buy less. This response shifts aggregate demand to the left.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most economists believe that money neutrality
A) does not hold in the short run.
B) does not hold in the long run.
C) does not hold in either the short run or long run.
D) holds in the short run and the long run.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can explain the upward slope of the short-run aggregate supply curve?
A) nominal wages are slow to adjust to changing economic conditions
B) as the price level falls, the exchange rate falls
C) an increase in the money supply lowers the interest rate
D) an increase in the interest rate increases investment spending
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Figure 33-13. 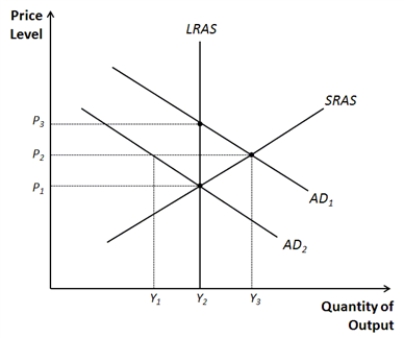 -Refer to Figure 33-13. Identify the price and output levels consistent with long-run equilibrium.
-Refer to Figure 33-13. Identify the price and output levels consistent with long-run equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the context of aggregate demand and aggregate supply, the wealth effect refers to the idea that, when the price level decreases, the real wealth of households
A) increases and as a result consumption spending increases. This effect contributes to the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
B) decreases and as a result consumption spending increases. This effect contributes to the upward slope of the aggregate-supply curve.
C) increases and as a result households increase their money holdings; in turn, interest rates increase and investment spending decreases. This effect contributes to the downward slope of the aggregate-demand curve.
D) decreases and as a result households increase their money holdings; in turn, interest rates increase and investment spending decreases. This effect contributes to the upward slope of the aggregate-supply curve.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the interest rate causes investment to
A) rise and the exchange rate to appreciate.
B) fall and the exchange rate to depreciate.
C) rise and the exchange rate to depreciate.
D) fall and the exchange rate to appreciate.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the price level rises, the interest rate
A) falls, so the supply of dollars in the market for foreign currency exchange shifts left.
B) falls, so the supply of dollars in the market for foreign currency exchange shifts right.
C) rises, so the supply of dollars in the market for foreign currency exchange shifts left.
D) rises, so the supply of dollars in the market for foreign currency exchange shifts right.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the early 1930s in the United States, there was a
A) large increase in output. In the early 1940s there was also a large increase in output.
B) large increase in output. In the early 1940s there was a large decrease in output.
C) large decrease in output. In the early 1940s there was a large increase in output.
D) large decrease in output. In the early 1940s there was also a large decrease in output.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Optimism. How is the new long-run equilibrium different from the original one?
A) both price and real GDP are higher
B) both price and real GDP are lower.
C) the price level is the same and GDP is higher.
D) the price level is higher and real GDP is the same.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since the end of World War II, the U.S. has almost always had rising prices and an upward trend in real GDP. This can be explained
A) only by technological progress.
B) only by money supply growth.
C) by technological progress and money supply growth.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Political Instability Abroad. What would the change in the interest rate created by foreigners wanting to buy more U.S. assets do to investment spending in the U.S.?
A) make it rise which by itself would increase U.S. aggregate demand.
B) make it rise which by itself would decrease U.S. aggregate demand.
C) make it fall which by itself would increase U.S. aggregate demand.
D) make it fall which by itself would decrease U.S. aggregate demand.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If aggregate demand shifts right, then eventually price level expectations rise. This increase in price level expectations causes the aggregate demand curve to shift to the left back to its original position.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would cause investment spending to decrease and aggregate demand to shift left?
A) a decrease in the money supply and an investment tax credit.
B) the repeal of an investment tax credit and an increase in the money supply.
C) a decrease in the money supply and the repeal of an investment tax credit.
D) an investment tax credit and an increase in the money supply.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 33-6. 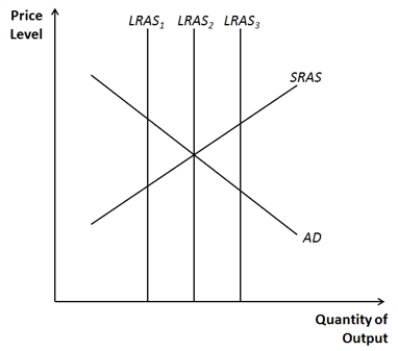 -Refer to Figure 33-6. Which of the long-run aggregate-supply curves is consistent with a recession?
-Refer to Figure 33-6. Which of the long-run aggregate-supply curves is consistent with a recession?
A) LRAS1
B) LRAS2
C) LRAS3
D) Both LRAS1 and LRAS3
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, if the price level rises, people
A) increase foreign bond purchases, so the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange increases.
B) increase foreign bond purchases, so the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange decreases.
C) decrease foreign bond purchases, so the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange increases.
D) decrease foreign bond purchases, so the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange decreases.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts right if
A) either immigration from abroad increases or technology improves.
B) immigration from abroad increases, but not if technology improves.
C) technology improves, but not if immigration from abroad increases.
D) None of the above are correct.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The investment component of GDP measures spending on
A) financial assets such as stocks and bonds. During recessions it declines by a relatively large amount.
B) residential construction, business equipment, business structures, and changes in inventory. During recessions it declines by a relatively large amount.
C) financial assets such as stocks and bonds. During recessions it declines by a relatively small amount.
D) residential construction, business equipment, business structures, and changes in inventory. During recessions it declines by a relatively small amount.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 441 - 460 of 572
Related Exams