A) there is a great demand for the good.
B) there is a competitive struggle to determine which firms will supply the market.
C) the regulated firm overstates its costs of production.
D) price is set at average total cost.
E) the rate is set too low.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rent seeking ________.
A) is a variable cost and with rent seeking the monopoly becomes more efficient
B) decreases average total cost and with rent seeking the monopoly becomes more efficient
C) increases deadweight loss above the original monopoly deadweight loss, but the monopoly continues to produce the same inefficient quantity
D) decreases consumer surplus and with rent seeking the monopoly becomes more efficient
E) decreases deadweight loss
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Methods of rent seeking include which of the following? I.Buying a monopoly II.Creating a monopoly III.Price discrimination
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) III only
E) II only
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 13.1.1
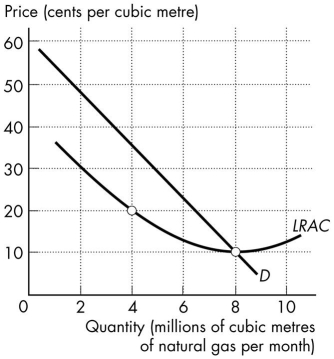 -Refer to Figure 13.1.1.The quantity demanded by the market is 8 million cubic metres a month.This market is
-Refer to Figure 13.1.1.The quantity demanded by the market is 8 million cubic metres a month.This market is
A) a legal monopoly.
B) served by a perfect price discriminating monopoly.
C) served by many firms each making an economic profit.
D) served by many firms each incurring an economic loss.
E) a natural monopoly.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal revenue curve for a single-price monopoly
A) is below its demand curve.
B) is the same as the demand curve.
C) lies above its demand curve.
D) is horizontal.
E) has a slope equal to the slope of the demand curve.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A single-price monopoly is a firm that ________ each unit of its output ________.A ________ monopoly sells different units of a good or service for different prices.
A) produces;at a constant cost;discriminatory
B) must sell;for the same price to all its customers;price-discriminating
C) produces;at a constant cost;price-discriminating
D) must sell;for the same price to all its customers;discriminatory
E) must sell;at the same price as a perfectly competitive firm;price-discriminating
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
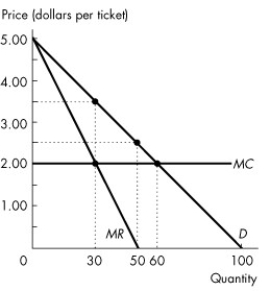 Figure 13.4.2
-Refer to Figure 13.4.2.Assume this monopolist practises perfect price discrimination.This means that
Figure 13.4.2
-Refer to Figure 13.4.2.Assume this monopolist practises perfect price discrimination.This means that
A) the monopoly's behaviour is illegal.
B) one price is charged to young people and a different price to older people.
C) a different price can be charged to each buyer.
D) price will rise as the number of buyers increases.
E) the quantity sold will be less compared to the case of no price discrimination.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs with both perfectly price-discriminating and single-price monopolies?
A) The amount of output is inefficient.
B) All consumer surplus goes to the monopoly.
C) Deadweight loss is created.
D) There is a redistribution of consumer surplus to the monopoly.
E) Demand is perfectly elastic.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is least likely to be a natural monopoly?
A) subway services
B) electric utilities
C) water and sewer services
D) taxicab service
E) cable television services
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under a marginal cost pricing rule,a regulated natural monopoly
A) makes an economic profit and a deadweight loss arises.
B) makes an economic profit with no deadweight loss.
C) incurs an economic loss with no deadweight loss.
D) incurs an economic loss and a deadweight loss arises.
E) breaks even.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
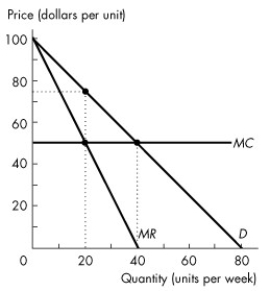 Figure 13.2.1
-Refer to Figure 13.2.1.This single-price monopoly produces ________ units per day and charges a price of $________ per unit.
Figure 13.2.1
-Refer to Figure 13.2.1.This single-price monopoly produces ________ units per day and charges a price of $________ per unit.
A) zero;0
B) 20;75
C) 40;50
D) 20;50
E) 20;20
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopolist can perfectly price discriminate,then
A) price equals average cost for each unit sold.
B) price equals marginal cost for each unit sold.
C) price equals marginal cost for the last unit sold.
D) the firm can ignore the marginal cost curve.
E) price is greater than marginal revenue for each unit sold.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Regulation of a natural monopoly will maximize the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus if the firm is regulated with
A) an average cost pricing rule.
B) a rate of return regulation.
C) a price cap.
D) capture theory.
E) a marginal cost pricing rule.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
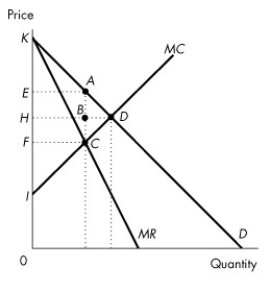 Figure 13.4.1
-A monopoly can practise price discrimination when it
Figure 13.4.1
-A monopoly can practise price discrimination when it
A) can segment the market according to the different prices the consumers are willing to pay.
B) is a price taker.
C) has different marginal costs of production for different output levels.
D) has decreasing average variables cost.
E) produces a good with close substitutes.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A perfect price-discriminating monopoly produces
A) less than a single-price monopoly.
B) more than a single-price monopoly but less than a perfectly competitive industry.
C) less than a monopoly that practices price discrimination but not perfect price discrimination.
D) more than a perfectly competitive industry.
E) the same amount as a perfectly competitive industry.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An average cost pricing rule sets ________ equal to average total cost.An average cost pricing rule is not an efficient way of regulating monopoly because at the quantity produced ________.
A) price;marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost
B) the return on capital;marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost
C) marginal cost;marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit
D) price equal to marginal revenue, which in long-run equilibrium is;marginal cost exceeds marginal benefit
E) marginal cost;marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the regulated natural monopoly,an average cost pricing rule sets price equal to
A) marginal cost.
B) total fixed cost.
C) average variable cost.
D) average fixed cost.
E) average total cost.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the demand for its good or service is elastic,a monopoly's
A) total revenue is unchanged when the firm lowers its price.
B) total revenue decreases when the firm lowers its price.
C) marginal revenue is positive.
D) marginal revenue is zero.
E) marginal revenue is negative.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist under rate of return regulation has an incentive to
A) pad costs.
B) produce more than the efficient quantity of output.
C) charge a price equal to marginal cost.
D) maximize consumer surplus.
E) maximize shareholder profits
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The capture theory holds that regulations are supplied to maximize ________.
A) total sales
B) economic profit
C) marginal product
D) consumer surplus
E) marginal revenue
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 107
Related Exams